Dosing
Appropriate Dosing of CroFab Achieves Initial and Sustained Control of Envenomation1
Snakebite treatment should be administered as soon as possible in patients with any sign of envenomation (e.g., local, systemic, or hematologic effects) to prevent clinical deterioration.1
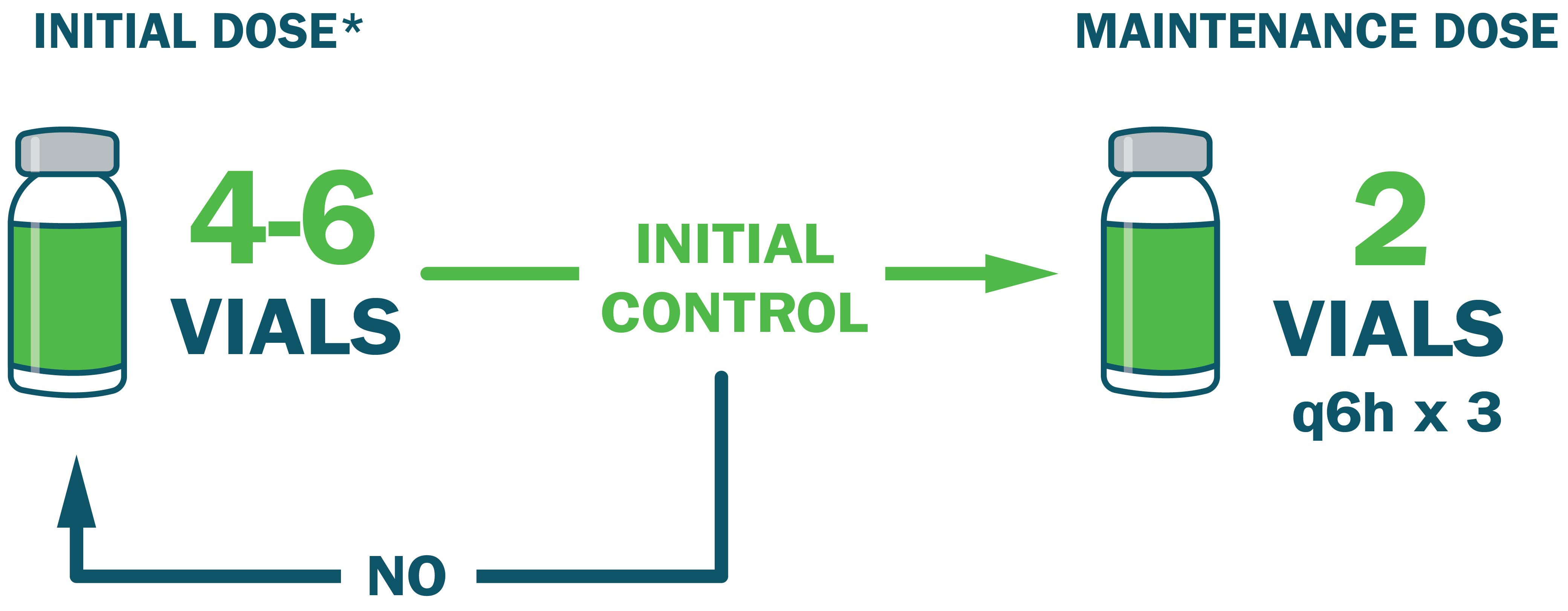
Administer an initial dose of 4-6 vials* and monitor for signs of progression.
- Administer an additional 4-6 vials if initial control is not achieved ~1 hour after initial dose
- Once initial control is achieved, administer an additional 2 vials every 6 hours for up to 18 hours (total of 3 doses)
- Scheduled maintenance dosing reduced the incidence of coagulation abnormalities due to residual venom1
*Initial dose may vary from 4-12 vials based on clinical judgment and severity of envenomation. Dosing is the same in adult and pediatric patients.1
In pre- and postmarketing studies, 67-88% of patients achieved initial control with an initial dose of 4-6 vials when given according to recommended dosing.2,3
Initial Control Requires Addressing All 3 Components of Envenomation1,4
Local
Effects
Progression of edema, ecchymosis, and leading edge of local injury has been arrested
Systemic
Effects
- Patient is normotensive and stable
- Neurotoxicity is resolving or improving
- Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or tachycardia is resolving
Hematologic
Effects
Coagulation abnormalities (e.g., thrombocytopenia, spontaneous bleeding) have normalized or are trending towards normal
Watch Dr. William Banner discuss his approach to dosing antivenom for children.
CroFab Clinical Studies
Review publications about achieving initial control of envenomation with CroFab
CroFab is reconstituted in 3 simple steps1
Real-world use supports improved outcomes with CroFab1
CroFab is clinically proven to achieve initial control of envenomation1