Safety Profile
CroFab Has an Established Safety Profile Backed by Over 20 Years of Clinical Experience1,2

Studied in adult and pediatric patients with envenomations of all levels of severity from all 3 species of North American pit vipers1
CroFab Was Designed to Reduce the High Incidence of Hypersensitivity Associated With Previous Antivenom Therapy3
Postmarketing data from 2 studies showed low rates of hypersensitivity reactions (1.4%; N=1340 and 2.7%; N=373) in patients treated with CroFab.4,5
Medically Significant Late Bleeding Is Uncommon After Treatment With CroFab6
In a systematic review of published postmarketing cohort studies, CroFab administration was associated with:
- Low rates of reported late bleeding*
- Low rates of medically significant late bleeding†
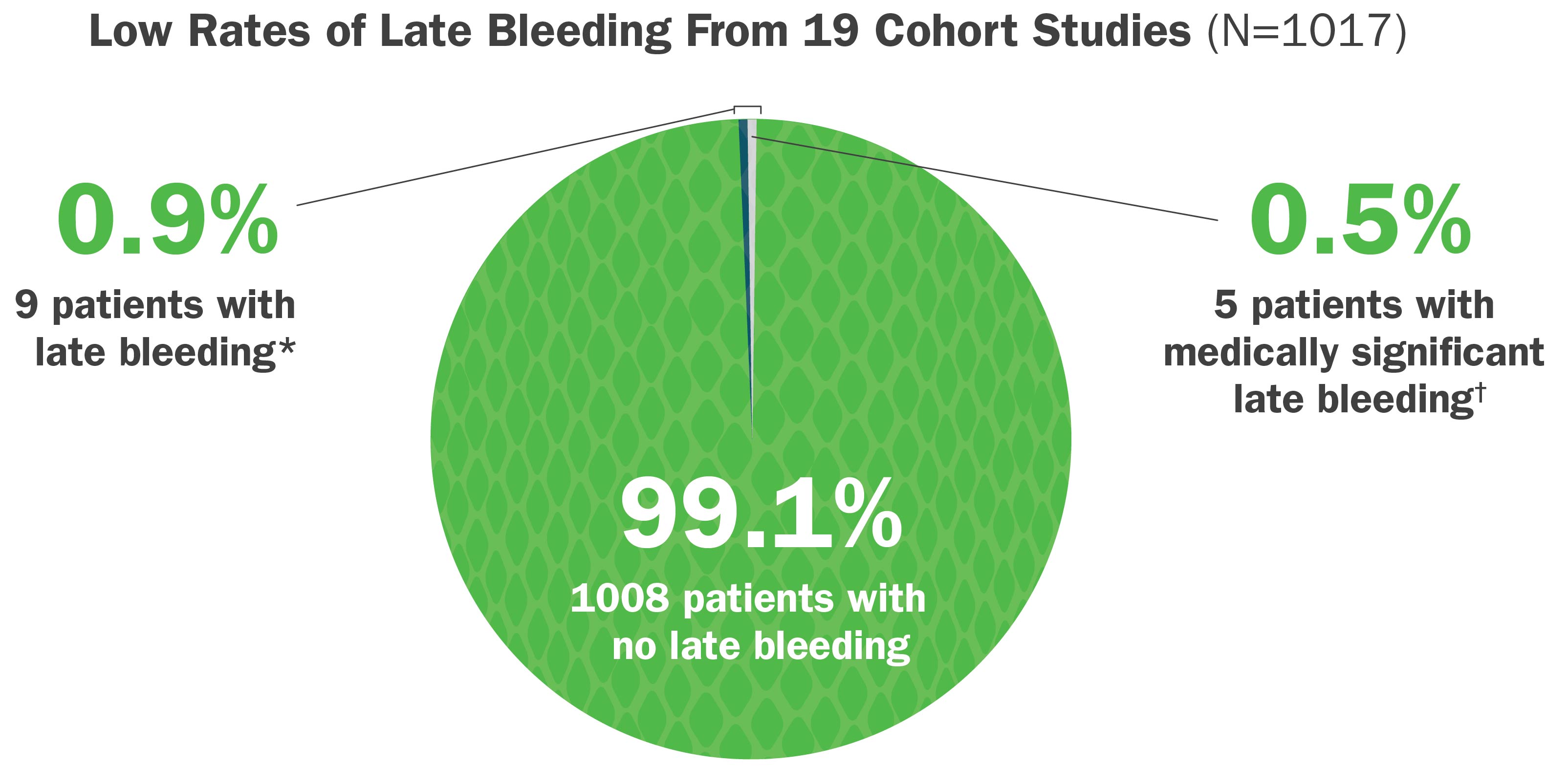
*A late bleeding event was defined as blood loss that was first noted after initial control of the envenomation syndrome, as defined by the study author or using standard criteria, was achieved.
†Medically significant late bleeding was defined a priori as any bleeding event associated with hypotension (systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg, or appropriate pediatric norms), significant tachycardia (pulse rate >140 beats/min or appropriate pediatric norms), a decrease in hemoglobin level ≥3 g/dL, or a decrease in hematocrit level ≥8 g/dL from previously measured levels, or treated with surgery, rehospitalization, or red blood cell transfusion.
CroFab Clinical Studies
Review publications evaluating efficacy and safety for CroFab
CroFab is clinically proven to achieve initial control of envenomation1
Appropriate dosing achieves initial and sustained control of envenomation1
Experts recommend stocking CroFab at any facility that provides emergency care7